3 Use cases how companies benefit from Smart Logistics Data

Transport damages to goods, delays in delivery, poor delivery reliability: These are three typical use cases in which Smart Logistics Data helps to identify and counter risks well in advance.
Smart Logistics Data form the basis for agile, robust and autonomous supply chains that anticipate and even avoid potential problems. In short, they are the foundation for efficient risk management.
Previously, we looked at how supply chain data can actually become intelligent and how we need to include production data as well as logistics data. Now, we illustrate how our customers can benefit from Smart Logistics Data specifically by looking at three use cases.
Use case 1: Anticipating transport damage – ensuring production quality
The quality of a manufactured product can only be as good as the quality of its components. Accordingly, companies must not only ensure that their own production processes run smoothly, but must also prevent defective parts from being assembled. But sensitive materials in particular can already suffer considerable damage during transport to the production site, which is either detected too late or not at all.
This is why one of our customers is now using Smart Logistics Data to monitor the transport of parts sensitive to temperature, humidity or vibration. For this purpose, we combine customer-related data on our platform, such as delivery call-offs, planning, orders, transport orders, etc., with IoT data that sensors transmit in real-time during transport. On well-structured dashboards, our customer can now detect potential transport damage almost in real time while the goods are still in transit.
By combining new and historical data from past deliveries, we provide risk forecasts. For example, the damage to be expected if certain suppliers transport certain goods on certain routes. The next step is to optimize planning in order to avoid these transport damages in the future.
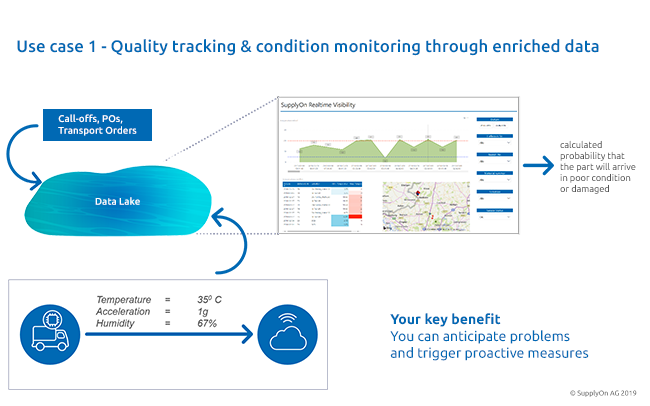
In short, Smart Logistics Data enables companies to anticipate delivery problems, initiate preventive measures, ensure the quality of the assembled components and thus improve production quality and customer satisfaction.
Use case 2: Detecting delivery shortages early on – adapting production planning
Production materials typically haul long distances before they arrive at the plant. As a rule, the means of transport changes several times along the transport route, often passing consolidation centers: From truck or rail it is shipped for several weeks, then back on the road again.
Usually there are several blind spots on such a route with unclear information about the current location of the goods. Particularly on sea, the situation is difficult to assess: Storms can take the ship off course. At the port, unloading can be delayed due to unexpected capacity problems. And a lot more can happen, which impairs the original Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) and thus disrupts the planning.
Until the company learns of this, however, it may take days or weeks. To maintain production, materials planners must rush to see if there are any material stocks left in a warehouse that can fill the gap. Alternatively, you can examine secondary procurement options, generally driving up procurement costs due to time pressure.
Such situations can be mitigated by Smart Logistics Data. Data such as demand information and consolidation data is fed into our data lake. This data is then enriched with further data, such as satellite information, with which the location of the ship can be pinpointed almost in real time.
On the basis of this location data and other information, we can then calculate whether the original arrival time (ETA) can still be met or whether the delivery will be delayed by days or even weeks. Our customer thus receives proactive alerts and can reschedule accordingly – in some cases even weeks in advance – while the materials are still on the sea.
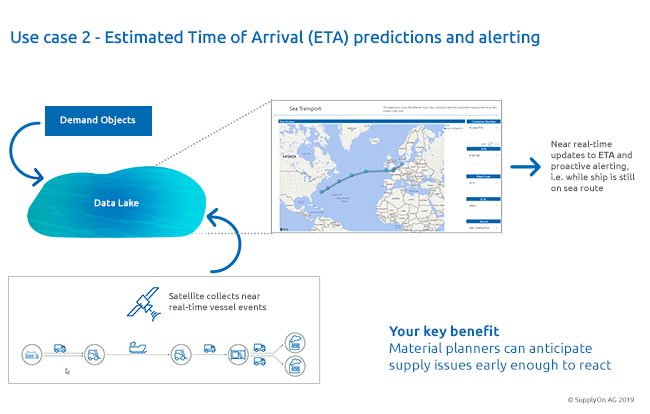
In short, problems can be identified at an early point using Smart Logistics Data. This provides valuable time to check alternatives promptly and minimize the impact on your own production.
Use Case 3: Analyzing delivery reliability – minimizing risks
Delivery delays and failures cause considerable financial damage. This is why more and more companies are taking a closer look: How reliable is my supplier? Will he actually deliver the agreed quantities within the agreed period? Is it possible that problems will arise again because he has already exceeded On-time Delivery (OTD) in the past?
Smart Logistics Data helps companies to precisely answer all these questions and thus minimize their risks. For this purpose, we enrich current customer data on requirements, demand collaborations and transports with historical data on supplier performance from our platform. In addition, data from supplier production (e.g. via MES integration) allows to derive further indicators.
We then use machine learning algorithms to analyze this data: Can we identify patterns? For example, on certain transport routes, from one plant to the other? Or for certain materials? And how likely is it that problems with this supplier and this order will occur again?
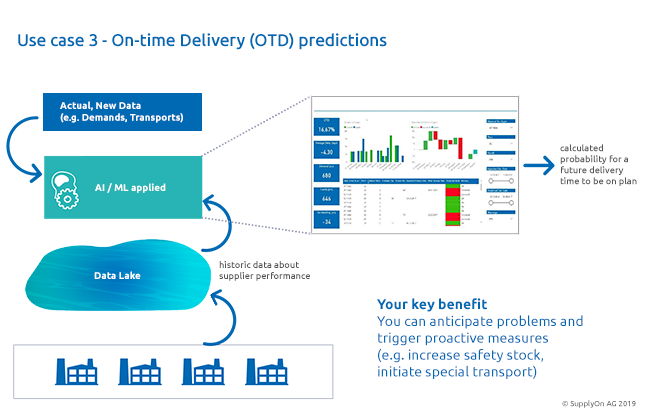
Bottom line: As in the other examples, you can see that it is a huge advantage being able to precisely contain risks by using Smart Logistics Data. This enables companies to proactively take measures to prevent shortages. In the case described, the company could increase the safety stock in the warehouse to have a larger buffer or order special deliveries to compensate for possible shortages.
Ultimately, suppliers benefit from Smart Logistics Data as well. How? Well, the results of the data analyses can also help them to identify their own deficiencies. On this basis, they can then develop solutions together with their customers, for example to accelerate the production cycles or to improve their planning horizon in the medium term.




